As a young person, a person has early symptoms of cartilage disease - bone necrosis.
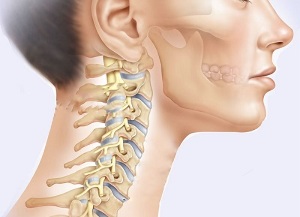
Typically, the first area affected is the cervical spine area, which can lead to disc herniation, as well as serious sensory and motor disturbances.
Therefore, it is not only necessary to know the symptoms of degenerative diseases of the neck spine of the spine, but also to diagnose them promptly.
Stages of cervical bone necrosis
The disease begins to develop - after 25 years - when cartilage metabolism deteriorates due to hormonal changes in the body. In this case, the blood supply to the disc spontaneously stops.
These changes in the spine correspond to the early stage of the disease, when there is no sign of cervical necrosis. However, a combination of additional factors (genetics, stress, early injury, etc. ) provokes further progression of the disease.
The next stage in the development of the disease is the stretching of the membrane of the disc - the fibrous sac. Due to the loss of moisture, the disc changes shape and "swells, " in medicine known as bulgeosis. At this stage, the first signs appear - throbbing pain in the neck, caused by the pressure of the disc against the nerve.
The onset of stage 3 of the disease is manifested by rupture of the membrane of the disc (fibrous ring) and the appearance of a herniated disc compressing blood vessels and nerve fibers. At the same time, sensory and movement disorders of the upper extremities, as well as the collar region, are involved in pain.
The transition to the fourth stage of the development of the disease is the complete destruction of the disc, when the blood supply not only to individual nerve fibers but also to the entire spinal cord ceases. The changes at this stage are irreversible, so surgical treatment is required.
General symptoms of the disease
A bone tumor can be diagnosed in one (or several) parts of the spine. At the same time, cervical spinal cord necrosis is considered particularly dangerous, since in this part of the spine are large vessels and nerve roots, which supply blood and nourish not only the hands but also the brain.
Thus, symptoms of cervical necrosis are divided into three large groups:
- Compression of the arteries:Normally we are talking about the vertebral arteries, which are in the processes of the cervical vertebrae and supply to the brain;
- Nerve root compression:is manifested by impaired mobility and sensation in the hands, as well as in the apical region of the skull and behind the head;
- Spinal cord compression:a variant of the IV stage of the disease, associated with severe neurological disorders (paralysis, lack of superficial sensations, etc. ).
The expressions described are generic. However, there are many personal symptoms that allow you to spot the disease in its early stages.
Pain
The first manifestation of fibroids of the cervix is local pain syndrome - cervical pain. This is usually a severe pain in the neck, sometimes spreading down the arm or back of the head. Pain occurs after incorrect postures (walking away during transportation, sleeping) or physical activity. Usually they overcome themselves.
After turning or tilting your head vigorously, low back pain may occur in the collar area (if not low back pain). Usually it is accompanied by muscle tension, so head movements become impossible (up to 10 days after the onset of the ankle).
Over time, an adaptation to the pain occurs. But at the second stage, the pain is often more intense, which indicates further displacement and destruction of the disc.
When the "convex" part of the disc reaches nerve fibers, radicular syndrome (also known as "radiculitis") occurs. Often accompanied by unilateral pain extending to the arm (as well as sensation and movement disturbances). In this case, a muscle tension reflex is observed - it is not possible to tilt the head.
Other variations of pain syndrome are:
- headache, often mimics migraines, but does not get better with conventional pain relievers. Usually it "diverges" behind the head, the apical and temporal regions, sometimes to the eyeballs. In this case, it can be single or double sided;
- "Heart attack" (or heart attack) is extremely rare. Presented by chest pain, which may resemble angina.
Be careful!If the cause of the chest pain is bone necrosis, then in this condition the "heart" medicine won't help! If these pills provide short-term pain relief, while still feeling a sense of fear of death, you should suspect a heart attack and go to hospital urgently.
Sensory disturbances in the neck spine
Loss, decrease or increase in sensitivity are the main symptoms of necrosis of the cervical spine. Therefore, sensory disturbances are often observed in the back of the head, as well as around the shoulder or hand joint.
In the latter case, these manifestations are accompanied by edema or other nutritional conditions (ulcers and other diseases).
Movement disturbances
If a disc herniation compresses motor nerve fibers, the patient may feel muscle weakness with limited range of motion - hemiplegia. The extreme degree of movement disorders is paralysis - complete lack of movement, as well as decreased muscle tone (until they atrophy) and loss of reflexes. Such symptoms in the early stages may be temporary.
Other Symptoms
The manifestations described above are classic symptoms of cervical osteonecrosis.
However, there are other (important! ) signs of the disease.
- Go Back. It is often accompanied by bone necrosis. Dizziness is related to a defect in the blood supply to the inner ear - a coupling balancing organ located in the temporal bone. Abnormal posture or periodic exacerbations of osteonecrosis cause dizziness, sometimes accompanied by fibrillation of the eyeball - the pupil is rapidly fluctuating. Balanced human organs are supplied with blood through an artery - the vertebral artery. It passes through the cervical vertebrae, and can therefore be "compressed" in diseases of the spine (with osteonecrosis, fractures).
- Ringing in the ears. Tinnitus or obstruction in the ear is another option that reduces the ability to "transport" blood to the inner ear. This symptom appears after lying in the wrong position for a long time, then disappears. This is the final symptom to differentiate a similar symptom in osteonecrosis from similar symptoms in other diseases.
- Nausea. It is an independent symptom, but it is sometimes accompanied by vomiting or vomiting. Then there is provocation by tilting and rotating the head, sometimes even walking. The reasons for this condition are the same as for dizziness - decreased distribution of arterial blood to the balance organ. However, prolonged vomiting can have serious complications - dehydration and salt loss in the body, which can lead to alkalosis (alkalosis of the blood). This requires intravenous administration of the appropriate saline solutions.
- Respiratory disorders. One symptom of cervical necrosis may be difficulty breathing when breathing becomes shallow (you cannot "breathe in through chest" completely). It causes a state similar to compression or over-stimulation of the phrenic nerve (it activates the diaphragm, the muscle responsible for respiratory movements). In such situations, the patient feels lack of air or difficulty breathing. Usually, however, overstimulation of the phrenic nerve is manifested by persistent hiccups.
- Night attacks. Holding your breath while sleeping in an unsuccessful position can also lead to osteonecrosis of the cervix. But the disease is usually manifested by snoring and morning lethargy due to lack of oxygen in the night sleep. Such "hypoxia" can lead to brain disorders - attention loss and memory loss.
- Sore throat. This is considered one of the most common symptoms of cervical necrosis. Its symptoms are dry throat, feeling of "foreign body", possibly itchy or difficult throat. This is due to compression of nerve and blood vessel bundles extending from the spine to the organs in the neck. In addition, we must not forget that similar symptoms may indicate other conditions (tumor or respiratory disease). At the same time, the presence of bone necrosis does not rule out tumor or inflammatory process.
- Visual disturbances. The visual organs are supplied with blood by both the vertebrae and the carotid artery. Therefore, vision changes with this pathology are less common, but they are characteristic of people with atherosclerosis or hypotension (low blood pressure). Among the possible symptoms are: "fog" or flashes of "flies" in front of the eyes, vision loss or disturbance in accommodation (focus). At the same time, the symptoms of the disease are unstable and cannot be corrected with optics (glasses, contact lenses) or gymnastics.
- Unstable pressure. When the vertebral artery is compressed, the blood supply to the vasomotor center can be disturbed, leading to inappropriately increased or decreased pressure. This can then be accompanied by fainting - syncope.
- Sinkope. Syncope is often observed in the elderly, who have atheroma plaques in the arteries. Usually, the vasoconstriction reflex (due to over-stimulation of nerve ends due to protrusion of the eye or bone process) leads to a sharp decrease in blood flow to the brain. As a result, the brain feels that lack of oxygen - lack of oxygen - is the cause of loss of consciousness. Be careful! In such situations, help for fainting involves a person being placed on a flat surface and his feet raised. Blood flows from the veins of the lower half of the body to the heart and then to the brain, for needed blood flow. To revive a person, it is recommended to use a substance with a pungent odor, for example, ammonia. People sometimes have speech and / or movement problems after fainting, but these symptoms are usually temporary due to a short fainting period. If the fainting persists for more than a few minutes and is followed by an anxiety headache, while these violations do not go away after a few hours, you should suspect the stroke and go urgently to the hospital.
- Rising temperature. This is a very rare symptom of cervical osteonecrosis. It occurs when blood flow is impaired in the hypothalamus (the calming center of the brain). After that, not only increases but also body temperature decrease. However, most often local phenomena are observed - congestion (redness and warming) in the collar area. Remember, the presence of osteonecrosis does not rule out an increase in temperature due to inflammation or swelling!
- Static violation. These are the postural curvatures, the "binding" of the curvature of the spine, as well as the compression in the joints of the spine. Such changes lead to a redistribution of the load, resulting in some parts of the spine (eg, lumbar) becoming overloaded. This can lead to the simultaneous development of osteonecrosis in other parts of the spine.
- Spinal stroke. As mentioned above, stage IV cervical necrosis can lead to spinal stroke (spinal cord injury). Such a pathology is extremely rare, but it is distinguished by its dangers: there is often hemiplegia (complete immobility of the arms and legs), no pain sensation and sensitivity to temperature atall limbs, sometimes eye shrinkage, drooping eyelids, pupil shrinkage, decreased facial sensitivity, etc. v. In such cases, immediate surgical intervention is indicated.
Prevention
To prevent disease development and complications, you need:
- for prompt treatment of spinal injuries (bruising and dislocation);
- corrects postural disorders (curvature, scoliosis, scoliosis), instability of the spinal segments, ligament apparatus;
- for orthopedic problems (clubfoot, flat foot), as well as for orthopedic shoes, with comfortable heels or special insoles;
- for normal weight loss;
- balances nutrition by increasing the level of micronutrients, fluids and foods containing collagen (jelly and bone broth);
- does not lead a sedentary lifestyle and limits physical activity at the same time;
- undergoes annual preventive tests (especially for those working in industries with increasing levels of vibration from moving machinery, equipment or machinery);
- athletes, bodybuilders, v. v. don't suddenly quit training.
The elderly need control for comorbidities (atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension). At the same time, it is necessary to eliminate bad habits (smoking, smoking), as well as avoid stressful situations that lead to nervous tension.
Remember that osteonecrosis is a progressive disease that does not go away on its own. Many patients are encouraged by remission (weak stage), which causes them to return to their old lifestyle and stop treatment. And this, in turn, greatly worsens the outcome of the disease. Therefore, if you notice symptoms of degenerative cervical spondylolisthesis, hurry to see a neurologist! After all, there is no better treatment than timely therapy!

























